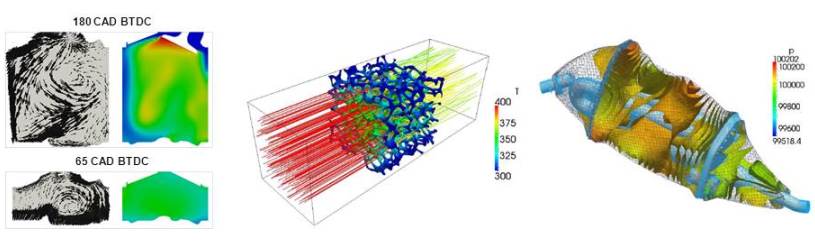
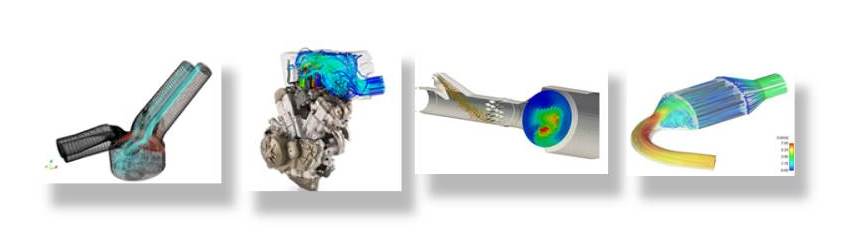
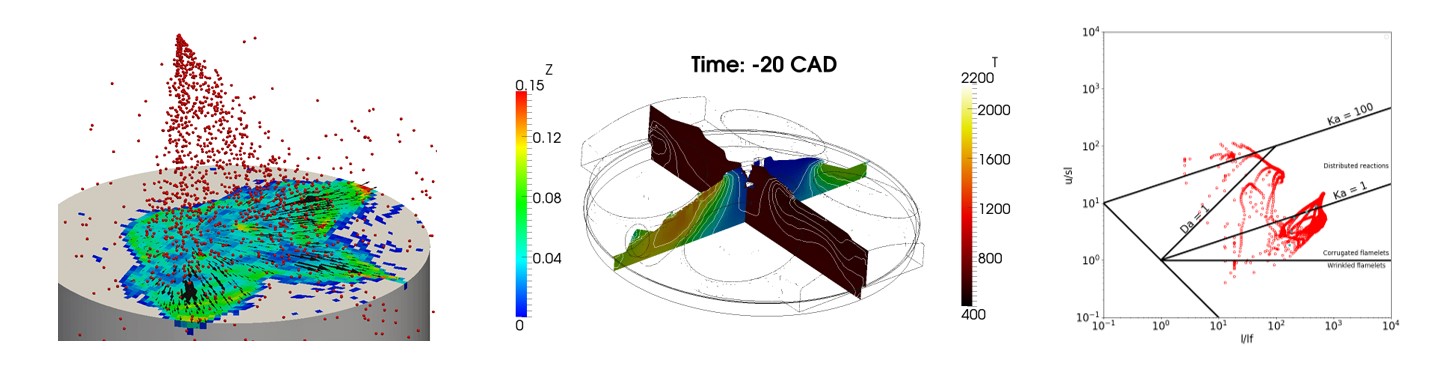
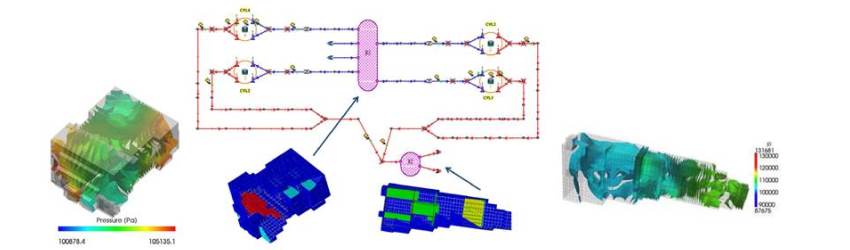
Premixed turbulent combustion
The current employed methodology to describe the combustion process occurring in a SI engine consists in a coupled approach between a flame propagation model and tabulated detailed chemical kinetics, such that it allows
to efficiently model conventional SI, SACI and dual-fuel combustion modes, including the prediction of the main pollutant emissions.
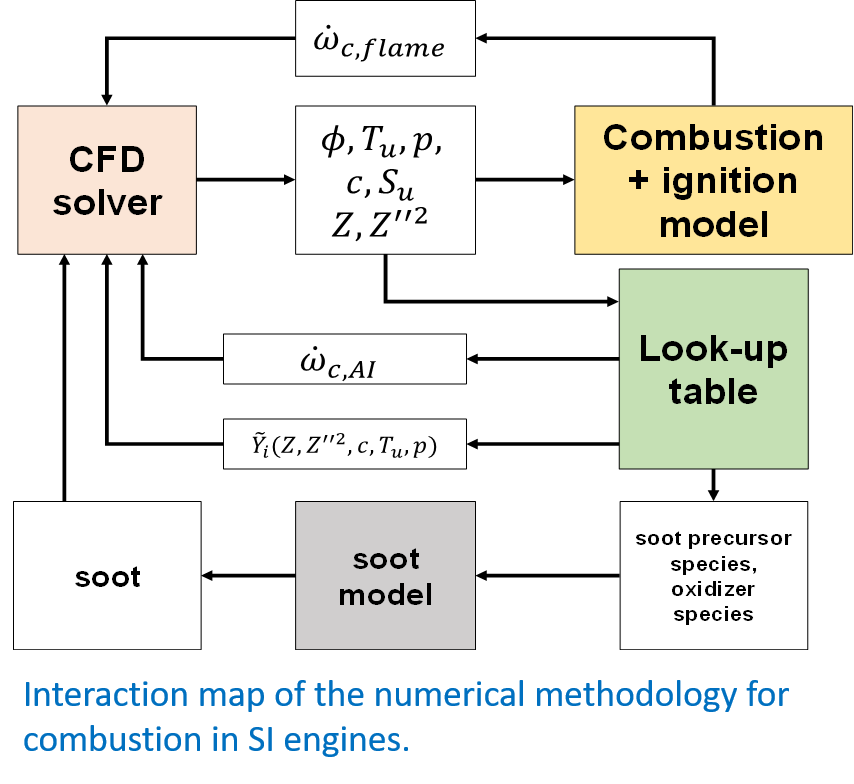
The main steps of the proposed combustion model, whose interaction map is reported in fugure, are the following:
- Thermo and fluid dynamic properties of the in-cylinder flows: solution of the main transport equations including mixture fraction and progress (regress) variable in the CFD domain.
- Ignition: deposition (energy/progress variable source term assigned by the user Different approaches) or Lagrangian model (arc or flame kernel are tracked using lagrangian particle. Each particle represents a possible location of a flame kernel).
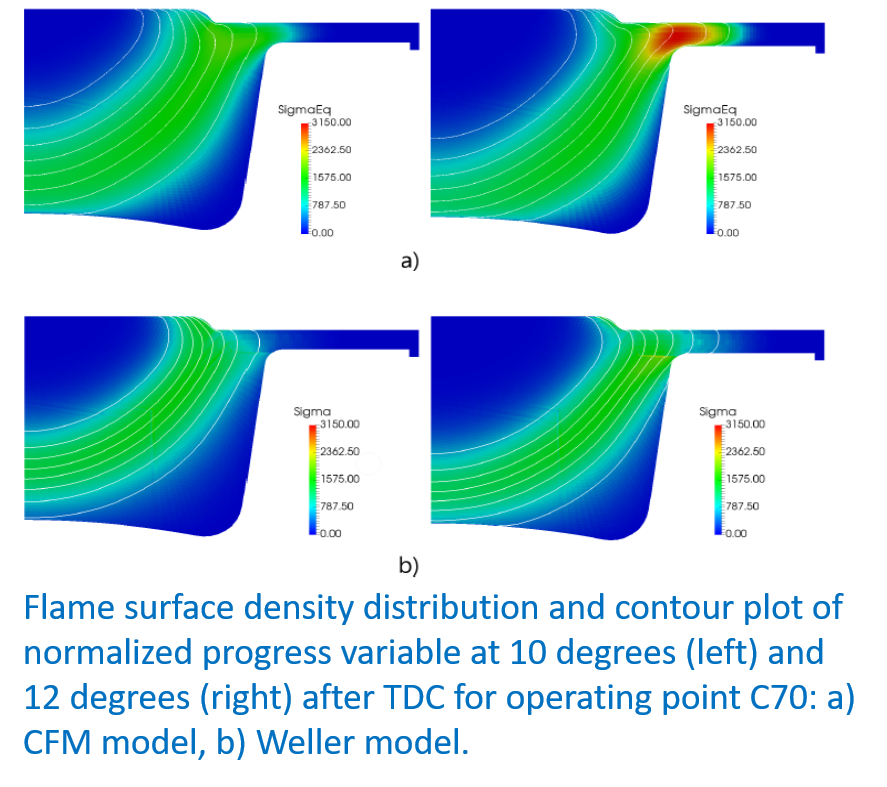
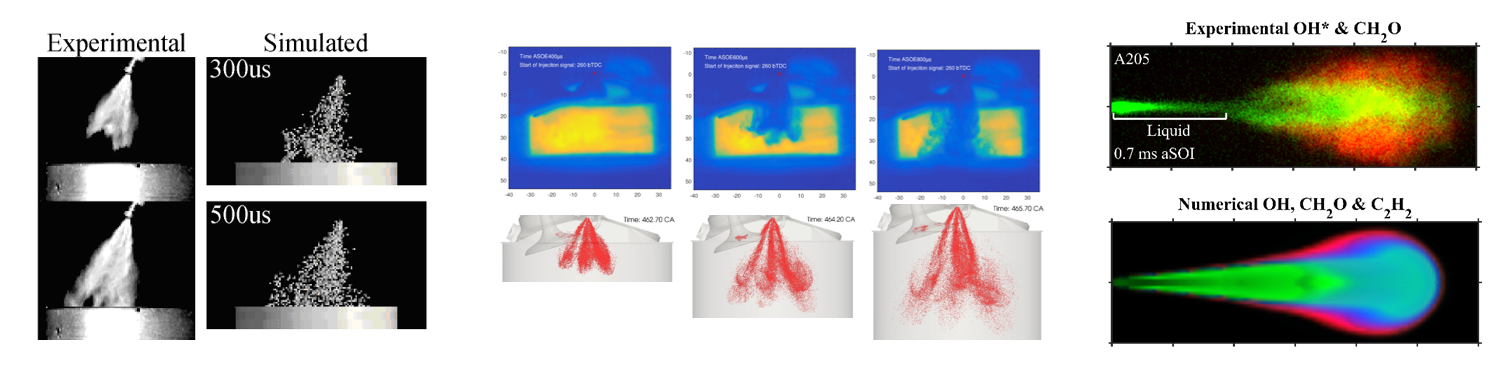
- Turbulent combustion: Weller or CFM model to describe turbulent flame propagation. The former solves a transport equation for a combustion regress variable, b, while reaction rate depends on an algebraic expression of the flame wrinkling factor.
- Gas chemical composition: tabulated kinetics applied to the burnt gases to include complex chemical mechanism and describe the formation of the main gaseous pollutant species and soot precursor species. Effect of mixture fraction fluctuations are taken into account.
- Soot formation: semi-empirical Leung-Lindstedt and Jones approach.